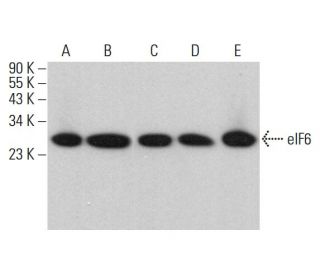
Anticorps eIF6 (A-12): sc-390441
- L'Anticorps eIF6 (A-12) est un monoclonal de souris mouse IgG1 κ κ, cité dans 3 publications, fourni en 200 µg/ml
- dirigé contre les acides aminés 1-245 correspondant à la séquence totale de eIF6 d'origine human
- recommandé pour la détection de eIF6 d'origine mouse, rat et human par WB, IP, IF, IHC(P) et ELISA
- m-IgG Fc BP-HRP et m-IgG1 BP-HRP sont les réactifs de détection secondaire préférés pour eIF6 Antibody (A-12) for WB and IHC(P) applications. Ces réactifs sont désormais proposés en lots avec eIF6 Antibody (A-12)(voir les informations de commande ci-dessous).
ACCÈS RAPIDE AUX LIENS
The initiation of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells is regulated by interactions between protein initiation factors and RNA molecules. Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are utilized in a sequence of reactions that lead to 80S ribosomal assembly and, ultimately, translation. eIF6 (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6) is also known as CAB, B2GCN homolog, p27(BBP) or B4 integrin interactor and is a 245 amino acid protein that is localized to the cytoplasm, as well as to the nucleolus within the nucleus. The eIF6 N-terminal and C-terminal subdomains are thought to contain important nucleolar localization sequences. eIF6 may be a regulator of ribosomal function and creation. eIF6 functions to bind and translocate the 60S ribosomal subunit from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, effectively preventing the 60S subunit from associating with the 40S subunit and inhibiting formation of the 80S initiation complex. The regulation of the formation of the 80S ribosomes also regulates transcription. Once translocated to the cytoplasm, the eIF6-60S ribosomal subunit complex is subject to phosphorylation via the RACK1/PKC pathway, an event that results in the dissociation of eIF6 from the 60S subunit. Upregulation of eIF6 is strongly associated with a variety of of cancers, such as ovarian cancer, suggesting that eIF6 may be involved in carcinogenesis.
Informations pour la commande
| Nom du produit | Ref. Catalogue | COND. | Prix HT | QTÉ | Favoris | |
Anticorps eIF6 (A-12) | sc-390441 | 200 µg/ml | RMB2422.00 | |||
eIF6 (A-12): m-IgG Fc BP-HRP Kit | sc-540802 | 200 µg Ab; 10 µg BP | RMB2715.00 | |||
eIF6 (A-12): m-IgG1 BP-HRP Kit | sc-542377 | 200 µg Ab; 20 µg BP | RMB2715.00 |

